Remark :
Model-View-Controller (MVC) Structure

Main program
The main program initializes everything and ties everything together.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
// structure/calc-mvc/CalcMVC.java -- Calculator in MVC pattern. // Fred Swartz -- December 2004 import javax.swing.*; public class CalcMVC { //... Create model, view, and controller. They are // created once here and passed to the parts that // need them so there is only one copy of each. public static void main(String[] args) { CalcModel model = new CalcModel(); CalcView view = new CalcView(model); CalcController controller = new CalcController(model, view); view.setVisible(true); } } |
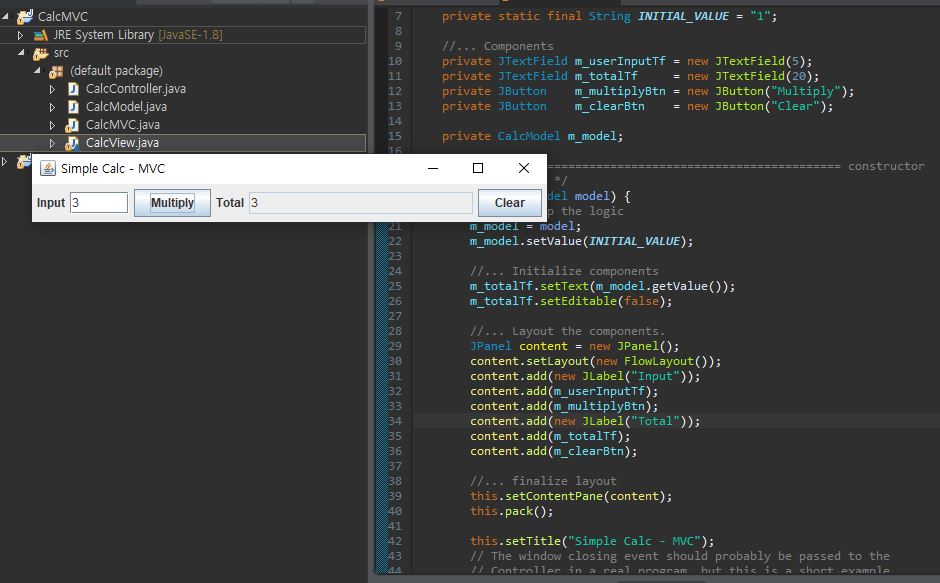
View
This View doesn’t know about the Controller, except that it provides methods for registering a Controller’s listeners. Other organizations are possible (eg, the Controller’s listeners are non-private variables that can be referenced by the View, the View calls the Controller to get listeners, the View calls methods in the Controller to process actions)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 |
// structure/calc-mvc/CalcView.java - View component // Presentation only. No user actions. // Fred Swartz -- December 2004 import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.event.*; class CalcView extends JFrame { //... Constants private static final String INITIAL_VALUE = "1"; //... Components private JTextField m_userInputTf = new JTextField(5); private JTextField m_totalTf = new JTextField(20); private JButton m_multiplyBtn = new JButton("Multiply"); private JButton m_clearBtn = new JButton("Clear"); private CalcModel m_model; //======================================================= constructor /** Constructor */ CalcView(CalcModel model) { //... Set up the logic m_model = model; m_model.setValue(INITIAL_VALUE); //... Initialize components m_totalTf.setText(m_model.getValue()); m_totalTf.setEditable(false); //... Layout the components. JPanel content = new JPanel(); content.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); content.add(new JLabel("Input")); content.add(m_userInputTf); content.add(m_multiplyBtn); content.add(new JLabel("Total")); content.add(m_totalTf); content.add(m_clearBtn); //... finalize layout this.setContentPane(content); this.pack(); this.setTitle("Simple Calc - MVC"); // The window closing event should probably be passed to the // Controller in a real program, but this is a short example. this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); } void reset() { m_totalTf.setText(INITIAL_VALUE); } String getUserInput() { return m_userInputTf.getText(); } void setTotal(String newTotal) { m_totalTf.setText(newTotal); } void showError(String errMessage) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, errMessage); } void addMultiplyListener(ActionListener mal) { m_multiplyBtn.addActionListener(mal); } void addClearListener(ActionListener cal) { m_clearBtn.addActionListener(cal); } } |
The Controller
The controller process the user requests. It is implemented here as an Observer pattern — the Controller registers listeners that are called when the View detects a user interaction. Based on the user request, the Controller calls methods in the View and Model to accomplish the requested action.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 |
// stucture/calc-mvc/CalcController.java - Controller // Handles user interaction with listeners. // Calls View and Model as needed. // Fred Swartz -- December 2004 import java.awt.event.*; public class CalcController { //... The Controller needs to interact with both the Model and View. private CalcModel m_model; private CalcView m_view; //========================================================== constructor /** Constructor */ CalcController(CalcModel model, CalcView view) { m_model = model; m_view = view; //... Add listeners to the view. view.addMultiplyListener(new MultiplyListener()); view.addClearListener(new ClearListener()); } ////////////////////////////////////////// inner class MultiplyListener /** When a mulitplication is requested. * 1. Get the user input number from the View. * 2. Call the model to mulitply by this number. * 3. Get the result from the Model. * 4. Tell the View to display the result. * If there was an error, tell the View to display it. */ class MultiplyListener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String userInput = ""; try { userInput = m_view.getUserInput(); m_model.multiplyBy(userInput); m_view.setTotal(m_model.getValue()); } catch (NumberFormatException nfex) { m_view.showError("Bad input: '" + userInput + "'"); } } }//end inner class MultiplyListener //////////////////////////////////////////// inner class ClearListener /** 1. Reset model. * 2. Reset View. */ class ClearListener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { m_model.reset(); m_view.reset(); } }// end inner class ClearListener } |
Model
The model is independent of the user interface. It doesn’t know if it’s being used from a text-based, graphical, or web interface. This is the same model used in the presentation example.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 |
// structure/calc-mvc/CalcModel.java // Fred Swartz - December 2004 // Model // This model is completely independent of the user interface. // It could as easily be used by a command line or web interface. import java.math.BigInteger; public class CalcModel { //... Constants private static final String INITIAL_VALUE = "0"; //... Member variable defining state of calculator. private BigInteger m_total; // The total current value state. //============================================================== constructor /** Constructor */ CalcModel() { reset(); } //==================================================================== reset /** Reset to initial value. */ public void reset() { m_total = new BigInteger(INITIAL_VALUE); } //=============================================================== multiplyBy /** Multiply current total by a number. *@param operand Number (as string) to multiply total by. */ public void multiplyBy(String operand) { m_total = m_total.multiply(new BigInteger(operand)); } //================================================================= setValue /** Set the total value. *@param value New value that should be used for the calculator total. */ public void setValue(String value) { m_total = new BigInteger(value); } //================================================================= getValue /** Return current calculator total. */ public String getValue() { return m_total.toString(); } } |
Source run